Biography
Official Biography
Since 2015, I have been a Lecturer at the School of Mathematics and Statistics, Technological University Dublin, teaching Statistics, Numerical Analysis and Mathematics to undergraduate and postgraduate students. I am also active in Science Communication, presenting at events such as Pint of Science, Bright Club, Maths Week, Science Week, and in schools. My research applies statistical and numerical methods to basic and clinical studies in Neuroscience, Neurology, and Optometry.
My background is in Mathematics (BA, MSc, PhD in Computational Fluid Dynamics, Trinity College Dublin, with John J. Miller). Seeking more applied work, I moved into postdoctoral research in neuroscience.
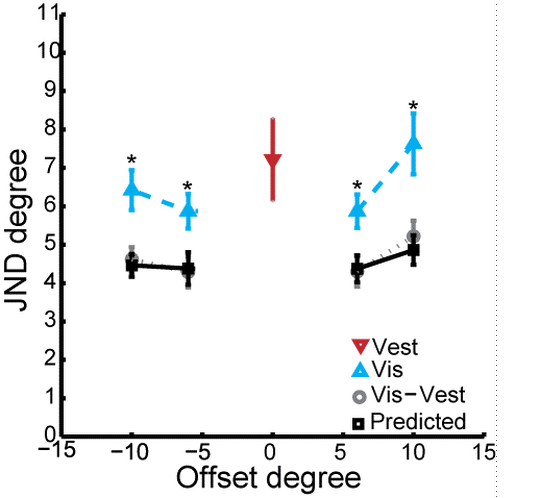
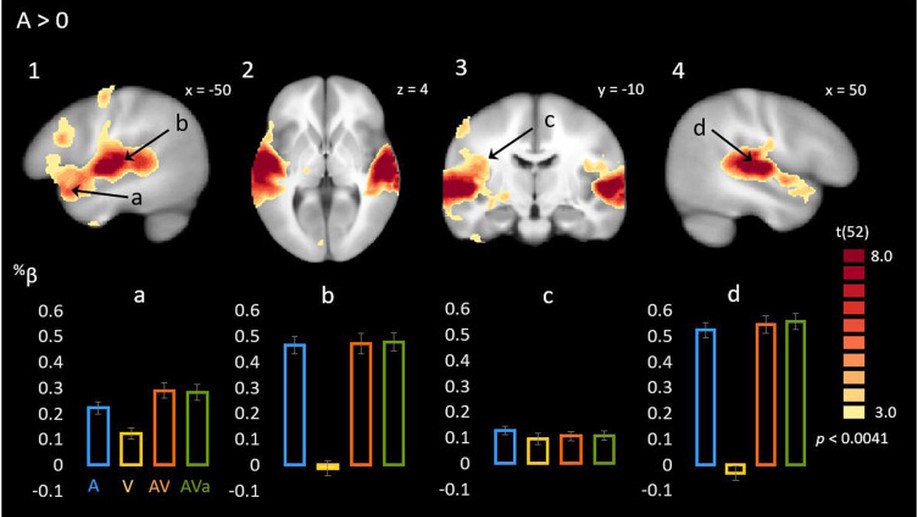
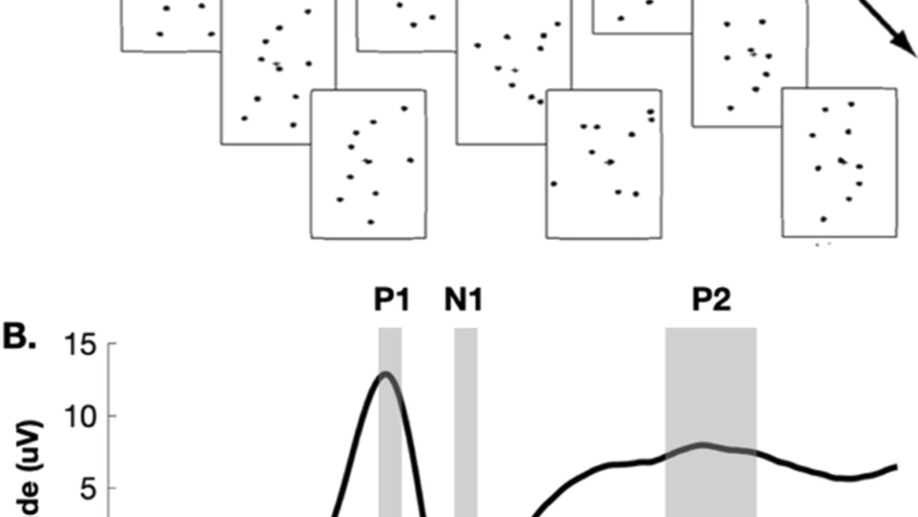
At the Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics, I worked with Heinrich Bülthoff on visual-vestibular integration using Virtual Reality, Psychophysics, and Bayesian methods. At the Albert Einstein College of Medicine (with John Foxe and Sophie Molholm), I studied sensory and multisensory integration and development in neurotypicals and people with Autism using behavioural and neuroimaging methods (EEG, ECoG, fMRI). I also helped establish a Mobile Brain Imaging (MoBI) VR lab for EEG during walking studies.
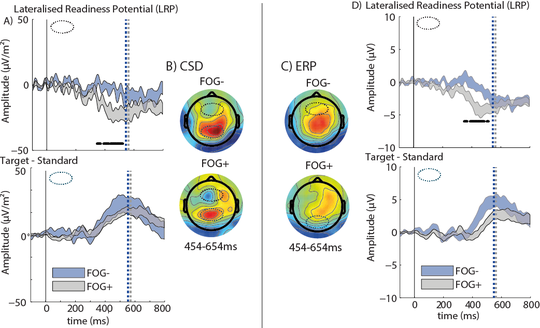
Later, at the Trinity Centre for Bioengineering, I worked with Richard Reilly as a postdoctoral fellow and lecturer in Neural Engineering, applying my methods to Parkinson’s Disease and Dystonia.
Here’s a video from the 2020 TU Dublin Virtual Postgraduate Open Day where I talk about my research interests:
Interests
- Neuroscience
- Computational Neuroscience
- Numerical Methods
- Statistical Methods
- Neurology
- Optometry
- Biomathematics
Education
-
PhD in Computational Fluid Dynamics, 2005
Trinity College Dublin
-
MSc in High Performance Computing, 2000
Trinity College Dublin
-
BA in Mathematics, 1999
Trinity College Dublin