An evaluation of the role of environmental factors in the disease penetrance of cervical dystonia
An evaluation of the role of environmental factors in the disease penetrance of cervical dystonia
Abstract
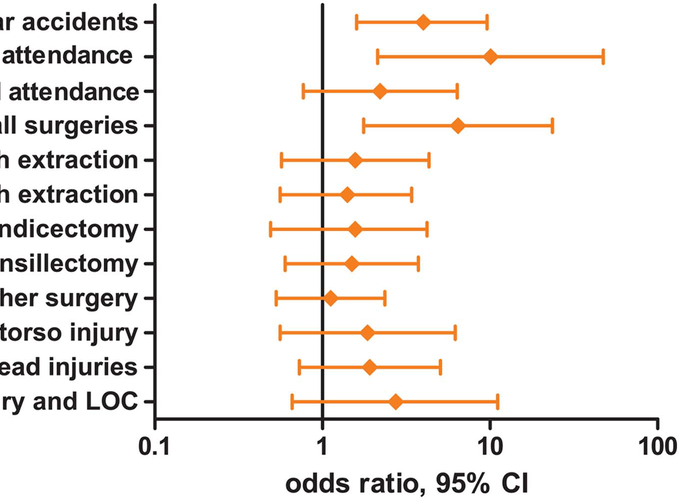
Background Adult onset primary torsion dystonia (AOPTD) is a poorly penetrant autosomal dominant disorder; most gene carriers are non-manifesting despite having reached an adequate age for penetrance. It is hypothesised that genetic, epigenetic and environmental factors may exert protective or deleterious effects on penetrance of AOPTD. By examining environmental exposure history in cervical dystonia patients and their similarly aged unaffected siblings we aimed to determine the role of previous environmental exposures in relation to disease penetrance. Methods A case-control study of 67 patients with cervical dystonia and 67 of their age-matched unaffected siblings was performed. Past environmental exposures were assessed using a detailed 124-question standardised questionnaire. Results By univariate analysis, cervical dystonia patients, compared to their unaffected siblings, had an increased frequency of a history of car accidents with hospital attendance (OR 10.1, 95% CI 2.1 to 47.4, p=0.004) and surgical episodes (OR 6.5, 95% CI 1.76 to 23.61, p=0.005). Following multivariate analysis, car accidents with hospital attendance (OR 7.3, 95% CI 1.4 to 37.6, p=0.017) and all surgical episodes (OR 4.9, 95% CI 1.24 to 19.31, p=0.023) remained significantly associated with case status. Conclusions Cervical dystonia patients had a history, prior to symptom onset, of significantly more frequent episodes of surgery and of car accidents with hospital attendance than their age-matched unaffected siblings. Soft tissue trauma appears to increase risk of development of cervical dystonia in genetically predetermined individuals.