Abstract
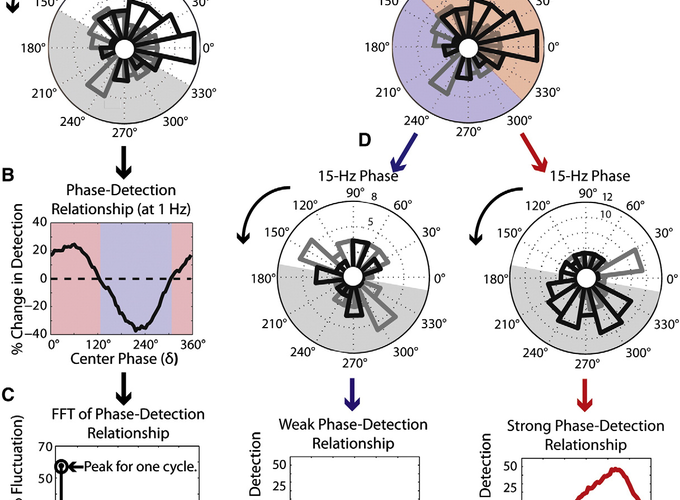
Functional networks are comprised of neuronal ensembles bound through synchronization across multiple intrinsic oscillatory frequencies. Various coupled interactions between brain oscillators have been described (e.g., phase-amplitude coupling), but with little evidence that these interactions actually influence perceptual sensitivity. Here, electroencephalographic (EEG) recordings were made during a sustained-attention task to demonstrate that cross-frequency coupling has significant consequences for perceptual outcomes (i.e., whether participants detect a near-threshold visual target). The data reveal that phase-detection relationships at higher frequencies are dependent on the phase of lower frequencies, such that higher frequencies alternate between periods when their phase is either strongly or weakly predictive of visual-target detection. Moreover, the specific higher frequencies and scalp topographies linked to visual-target detection also alternate as a function of lower-frequency phase. Cross-frequency coupling between lower (i.e., delta and theta) and higher frequencies (e.g., low- and high-beta) thus results in dramatic fluctuations of visual-target detection.